I am a big fan of GPS, and I’m not saying we should ditch this technology. (I mean, it might be worth tens of billions of dollars to the global economy). But here’s the question you should ask yourself next time you plug your destination into your phone instead of trying to figure things out with good old mental maps and landmarks: what have you lost by letting go of your sense of direction?
Technology has fundamentally changed the way we think of “direction”. Paul Puliot, the speaker for the Cowasuck band of the Abenaki people points out that the words for east and west in the Abenaki language actually refer to the location of the sun. “We were either traveling into the sun away from the sun or into the sunset,” he says.
Whereas we might think of direction in relation to our bodies, people used to think about direction in relation to the planet. There are actually whole languages that don’t have words like ‘left’ and ‘right’. Instead, if they were going to warn you of danger they might say, “Hey, watch out for that snake to the north of your foot!” And you’d just know where that snake was, because you just know… because you’d been paying attention, your whole life, to which way was which. You’d never get disoriented.
The good thing is, it’s not too late to start paying more attention to the world around you, and develop your navigational skills.
John Huth, a professor of particle physics at Harvard, decided he would learn how to navigate after being enveloped in a thick fog while kayaking in the Gulf of Maine. He managed to make his way to the shore, but the next day saw on the news that two other paddlers were caught in that same fog, got lost and died. Now he says, “I can look up in the sky and without having to name the names of stars or even having to think about it, I can find my way.” The need to exercise conscious thought to know which direction is which has fallen away.
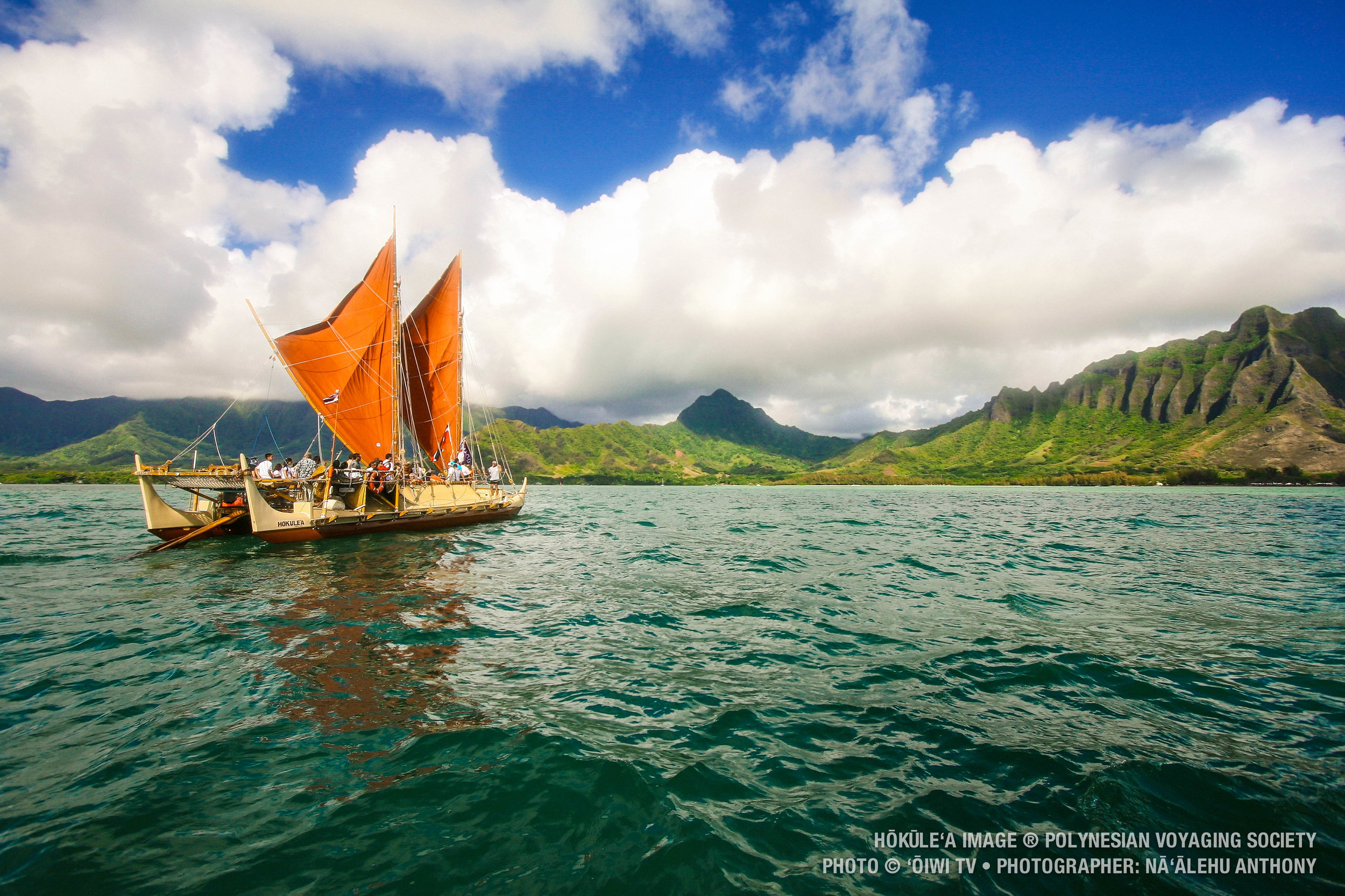
Bruce Blankenfeld, who sailed on the Hōkūleʻa during its first few voyages and subsequently went on to become a master navigator himself, describes a similar awakening. “I remember looking at the sky as a youngster and all you’d see is like billions of dots of light up there,” he explains, “But now, you’re looking at a definite map, you know.”
I’m not suggesting that you never turn your GPS on ever again. But consider leaving it off occasionally, and starting to pay more attention to the natural cues that indicate which way is which. Maybe if you do, you’ll start to get your sixth sense back.